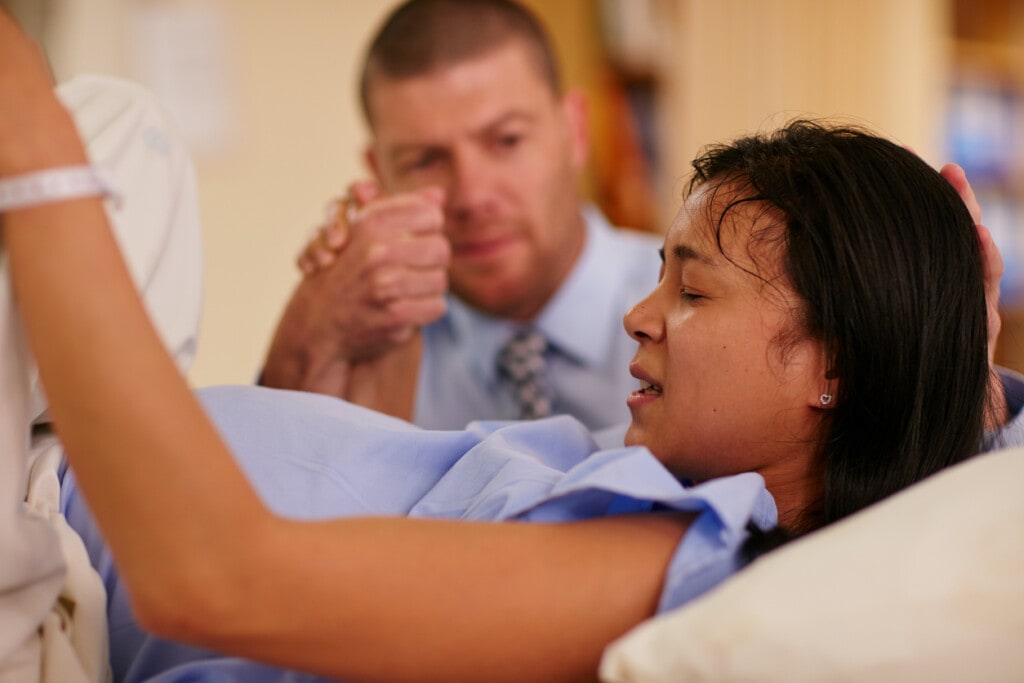
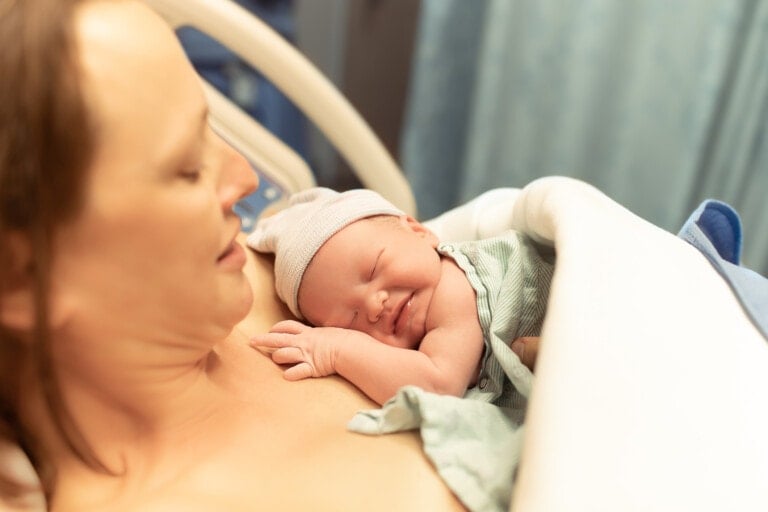
I remember going into labor with my first child like it was yesterday. My water broke, and the contractions came fast and quick. I was overcome with nausea and the pain of contractions as my husband grabbed our overnight bags, called my doula, and drove us to the hospital in a rush. When labor began, and I was pushing our daughter out, I was grateful that I knew what medical interventions I might need for pushing. I was grateful that we had a written birth plan, had taken childbirth classes together, and had hired a doula who was by my side advocating on my behalf during labor and delivery. The prior knowledge of medical interventions I might need during delivery made me feel more confident. It also made the whole process of my labor and delivery go smoother.
One unexpected situation arose from the intense pain and continuous vomiting I experienced after my water broke and contractions started fast and hard. Though I planned to have a natural birth, the pain of giving birth to my first child was so dramatic that I opted to get an epidural. It’s a decision I’ve never regretted and which I did for my second child’s birth, as well.
Medical Interventions You May Need During Pushing
You may have heard about medical interventions that can occur during labor, such as induction via membrane sweep, Pitocin, or an amniotomy. But do you know what medical interventions you might need during actual pushing? I was glad I had a doula to explain these to me before I delivered my children. Read on to learn more.
Epidural
An epidural is a spinal anesthetic given to mothers during childbirth to relieve pain. Epidurals are the most common type of pain relief used during childbirth in the U.S. Epidurals are usually administered when the cervix is dilated to 4-5 centimeters and given by an anesthesiologist. Intravenous (IV) fluids will be started before an epidural is placed. An obstetrician or nurse anesthetist will administer the epidural through the IV/catheter process.
I used an epidural with both of my deliveries. My daughters were delivered just fine, my recovery was normal, and both my daughters breastfed beautifully. For the birth of my first child, I had written in my birth plan that I didn’t want an epidural. But I never regretted getting one once my pain reached levels I couldn’t handle without medicine. Each woman is different, however. Making a birth plan with your specific preferences and goals for delivery—and then being okay if they need to change—can be a helpful way to make your birthing process smoother.
Episiotomy
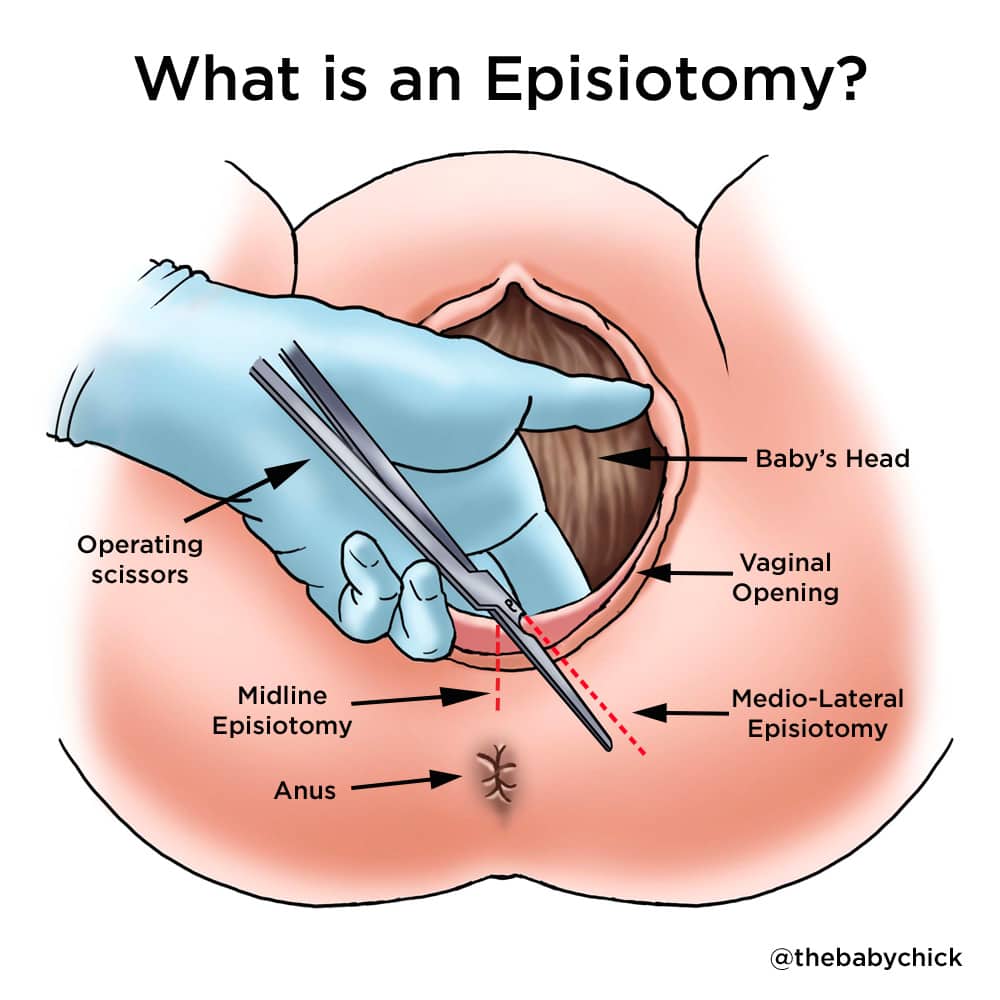
Episiotomies in childbirth used to be the norm. However, the past few decades of research have revealed that surgical cuts may not be as beneficial as medical professionals once believed.1
The episiotomy will be made in the perineum right before the baby’s head comes out. This is the area between the vagina and the rectum. The doctor will stitch up a small cut or incision after delivery. At my request, my obstetrician allowed my perineum to tear naturally during childbirth. Then she stitched it up afterward. I was glad we did it this way. My perineum healed normally without infection, and the natural tear was not severe.
Generally, an episiotomy is not needed in a healthy birth without any complications. But suppose there are complications during delivery that endanger the mother or baby. In that case, an episiotomy may be needed to ensure a faster delivery or to protect the child’s safety.
Fetal Monitoring

Fetal monitoring is a technique used for checking the baby’s heart rate. Auscultation is fetal monitoring done using a stethoscope/fetoscope or Doppler transducer to listen to the baby’s heart rate. This is the same equipment an obstetrician uses during prenatal visits. Electronic monitoring records the baby’s heart rate via a fetal monitoring Doppler belt placed around the abdomen. Internal monitoring requires an electrode to be placed on the part of the baby closest to the cervix, usually a baby’s scalp.
Changes in a baby’s heart rate can indicate a problem, such as the baby not getting enough oxygen. Fetal monitoring can help medical professionals determine if a C-section is necessary. I recall having the Doppler bands around my belly both times I gave birth. They didn’t bother me, and I hardly noticed them. I was glad to know that my child’s heart rate was being monitored. If a mother is wearing a Doppler band and feels uncomfortable, a nurse can help adjust the band for improved comfort.
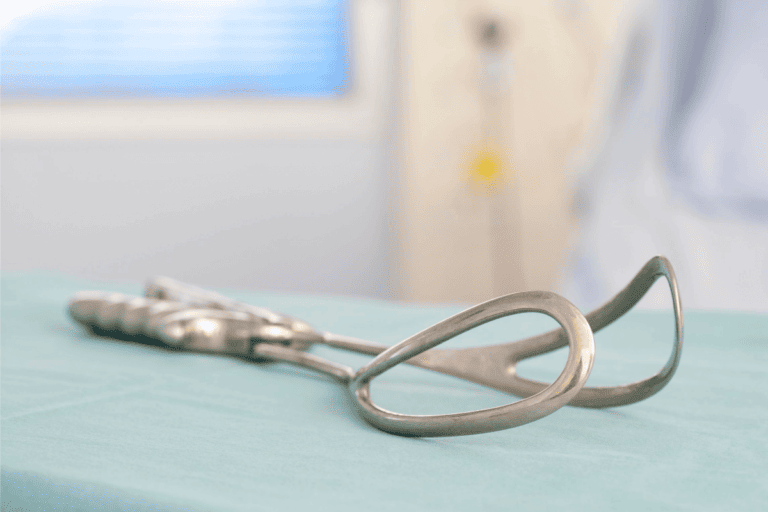
Forceps
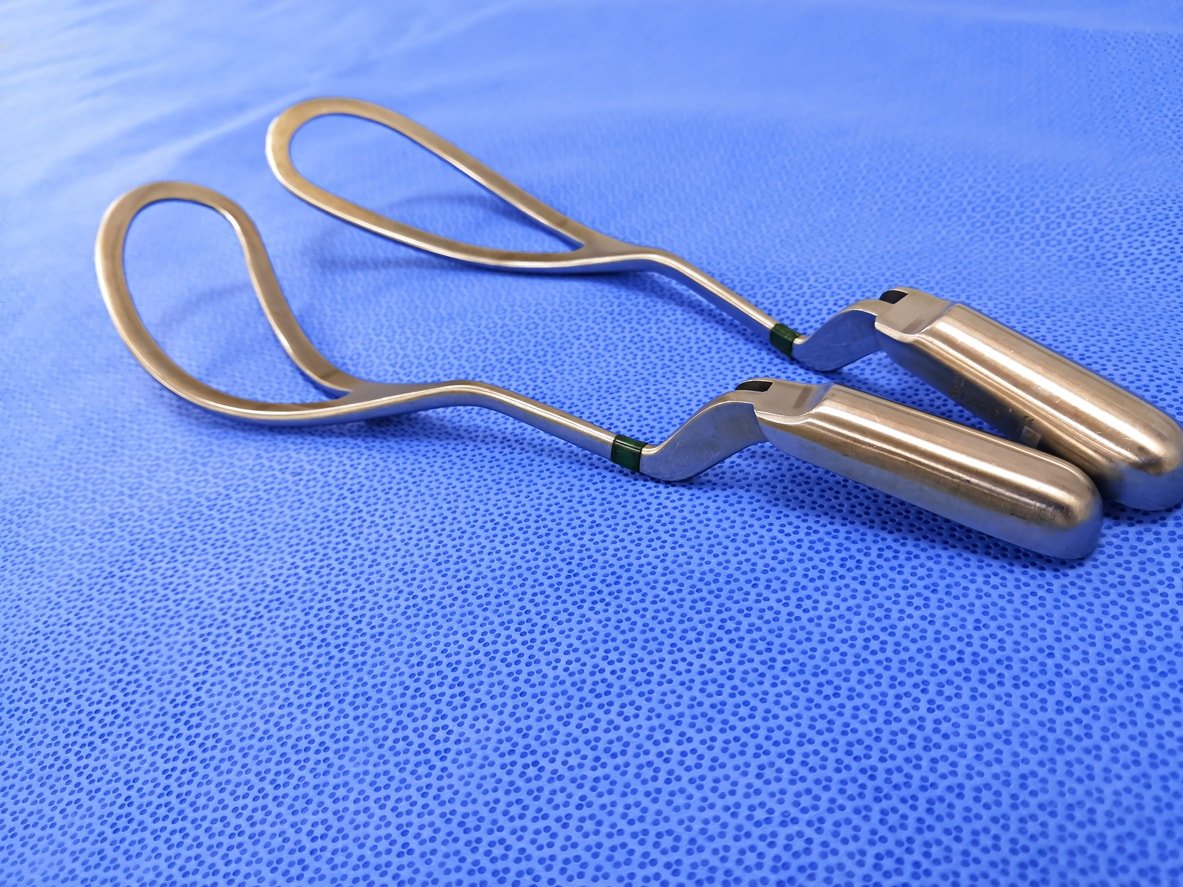
Forceps interventions are rare during delivery, used in only .56 percent of live births.2 A doctor may use them if the mother or baby shows signs of distress and delivery needs to be sped up. A forceps delivery occurs once the mother is fully pushing and can be an alternative to having a C-section if there is fetal distress.
A mother’s cervix must be fully dilated, and membranes must be ruptured. An episiotomy will likely be performed, and anesthetizing the area unless an epidural has already been administered. Between contractions, your obstetrician will insert the forceps into the vaginal canal, placing each forceps on either side of your baby’s head. As you push, the doctor will use the forceps to guide the baby out of the birth canal gently. You can push the rest of the baby’s body out as soon as the head is delivered. Bruising of the baby’s head and, in rare cases, bleeding or facial nerve damage may occur, making forceps a less-than-desirable choice but certainly worthwhile if necessary.
Vacuum Extraction
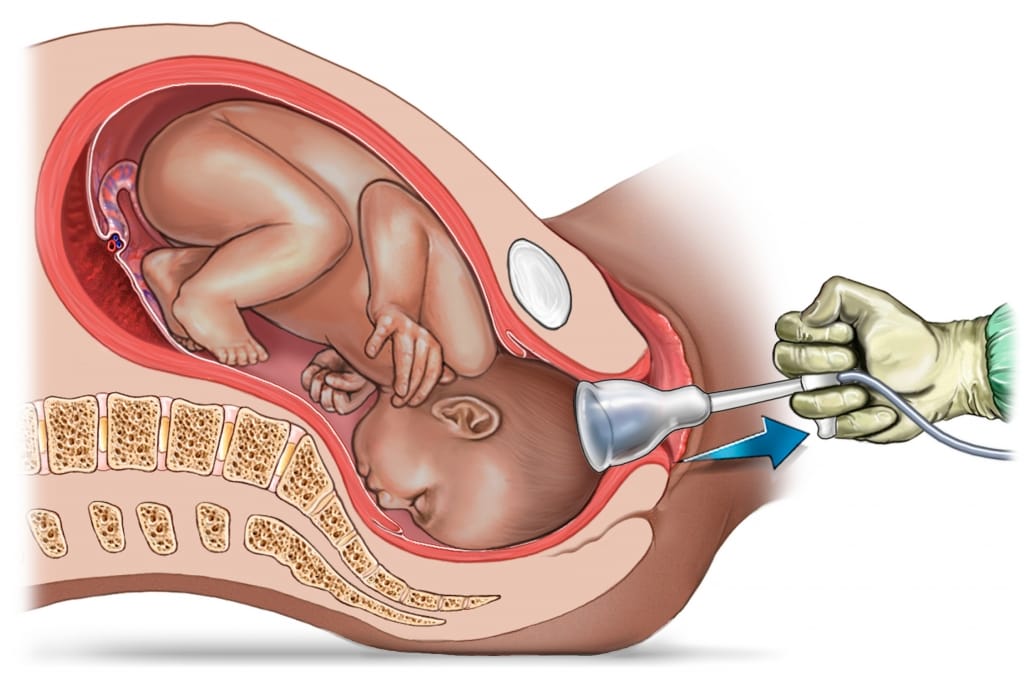
Like forceps, vacuum extraction is another type of assisted delivery that may be necessary if the baby is distressed and the delivery is stalled. For example, a vacuum extraction may be done if the labor is no longer progressing and the baby is stuck in the birth canal. Another example is if a mother is too tired to push, has a heart condition, or has very high blood pressure. Or if the baby is experiencing distress as indicated by a change in heart rate.
A vacuum procedure is performed in such a way that the doctor will place a vacuum extraction cup onto the baby’s head between a mother’s contractions. During the contractions, the doctor will use the vacuum pump to create suction to move the baby through the birth canal and prevent the baby’s head from moving back up between contractions. The doctor can remove the suction cup once the baby’s head comes through. The mother can push the rest of the baby’s body out. Vacuum procedures are more common than forceps delivery.2 But it’s more likely an obstetrician will go with a C-section instead of vacuum extraction if the delivery process has stalled.
C-Section
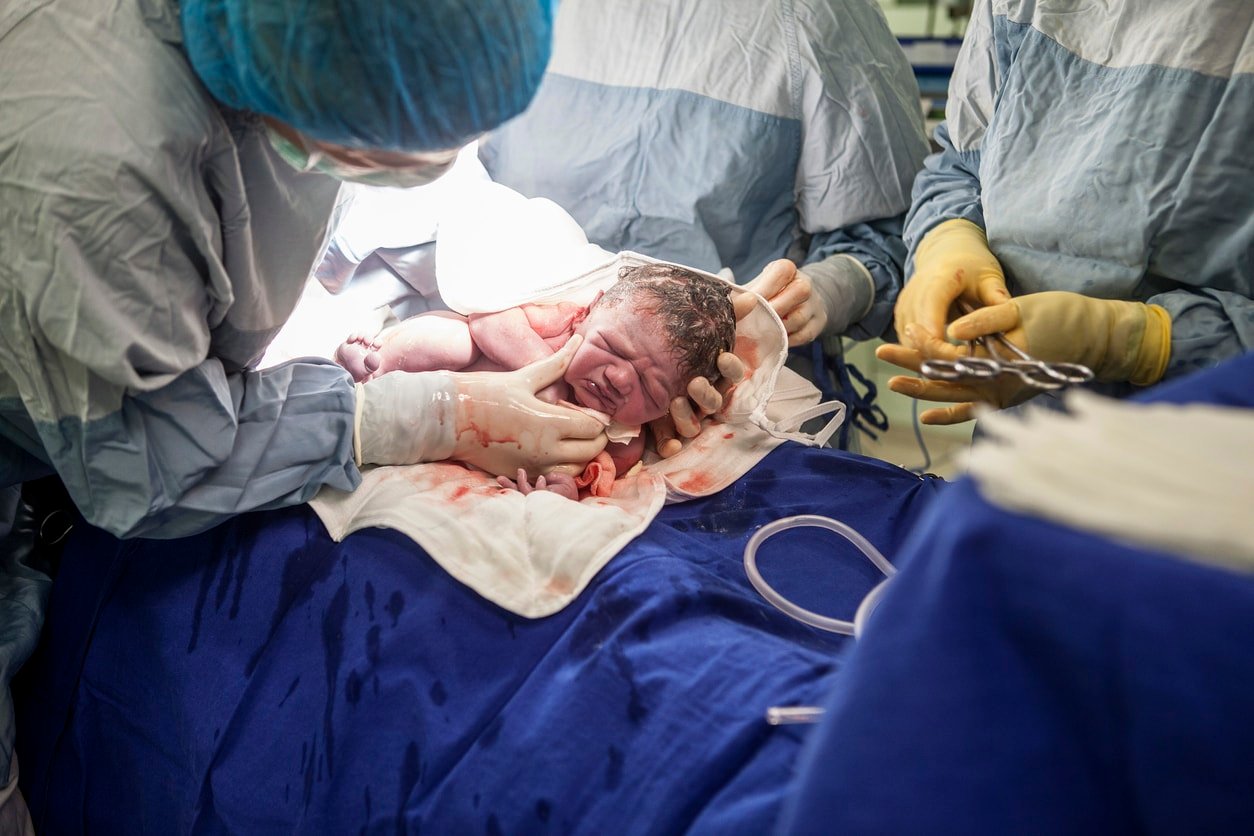
A Cesarean section, or C-section, is a surgical procedure to deliver a baby through an incision in a mother’s abdomen. This is an option if a mother has been pushing but the vaginal delivery is not progressing. Examples of transitioning from a vaginal delivery to an emergency C-section include problems with the umbilical cord wrapped around the baby, a change in the baby’s heart rate causing distress, concerns for the mother’s health, twin or multiples delivery, or other medical emergencies.
The procedure requires anesthesia to numb the lower half of the mother’s body, such as regional anesthesia, allowing the mother to remain awake during surgery. Common choices for numbing the pain include a spinal block or epidural block. Sometimes, general anesthesia is needed for an emergency C-section. While it typically takes longer to heal from a C-section than a vaginal birth, it can be a life-saving measure.
How to Avoid Interventions During Pushing
While it’s impossible to be certain you won’t need medical interventions during pushing, there are ways to lower your risk. And don’t worry if you need medical intervention. Childbirth is about the process, not perfection!
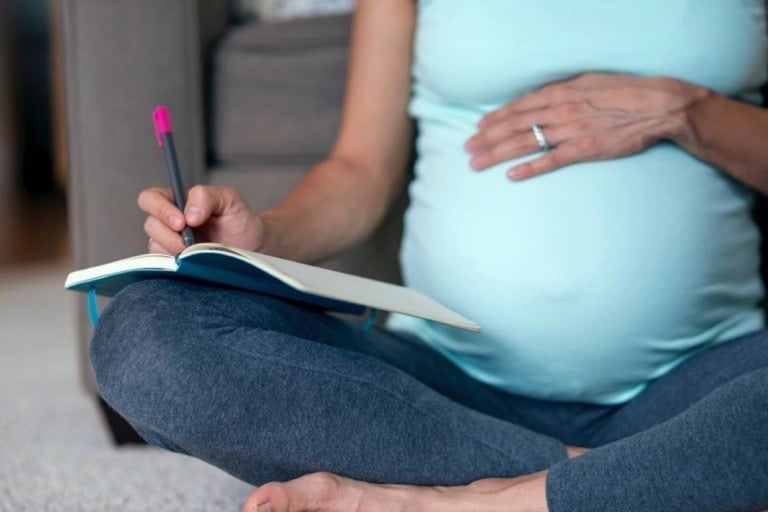
Write a Birth Plan

Taking the time to write out your birth plan will give you prior knowledge about what to expect. And it will help you to clarify what you want to occur during your labor and delivery. Writing a plan isn’t about ensuring it will go exactly as planned down to the last detail. Instead, one aims to get most of their goals down on paper and then share them with medical professionals performing the delivery. Many moms report that having a birth plan gave them confidence and authority over their labor and delivery. This kind of positive visioning may assist in making the birthing process go more smoothly.
Take a Childbirth Course

Enrolling in classes during pregnancy, like a childbirth class, can help the mother and her partner or delivery companion learn what to expect. The more knowledge a mother possesses, the better she can make choices or ask for what she needs during labor and delivery. This is also helpful for those assisting in her delivery, such as family members.
Work With a Midwife or Doula

A midwife usually works at a birthing center or the mother’s home for the delivery. A midwife’s care and expertise may reduce a woman’s risk for medical interventions.3 A doula is a childbirth advocate who can help you write your birth plan, meet with you before and after your delivery, and be present in the delivery room if you choose to have your baby at a hospital.
Some of these medical interventions are more common than others. By having a better understanding of each, we hope that you feel more prepared and more confident for your birthing day.