Placenta encapsulation. If you’re expecting, I’m sure you’ve heard a few people talking about it. Some people love and rave about it, while others think it’s weird and gross. But some people don’t know what it is. What is placenta encapsulation, and what are the pros and cons?
First, the placenta is an organ that develops on the uterus wall during pregnancy. It provides nutrients, blood, and oxygen to the baby while removing waste from the mother. Think of it as a filter, but it’s also your baby’s lifeline.
You may think you are done after pushing and giving birth to your baby, but you’re not. You then have to deliver the afterbirth, which is your placenta. Once the placenta is out, you can discard it or keep it. But why would anyone want to keep it? Well, some people keep the placenta for religious beliefs.1 Some plant it in their yard with a tree. Other people eat their placenta by cooking it, putting it into a smoothie, or encapsulating it. Many people believe the placenta offers benefits that help with recovery after birth. It is a controversial practice, and the CDC and Mayo Clinic discourage ingesting the placenta.2,3,4 However, it has gained popularity in the United States over the past few decades.
So, what is placenta encapsulation?
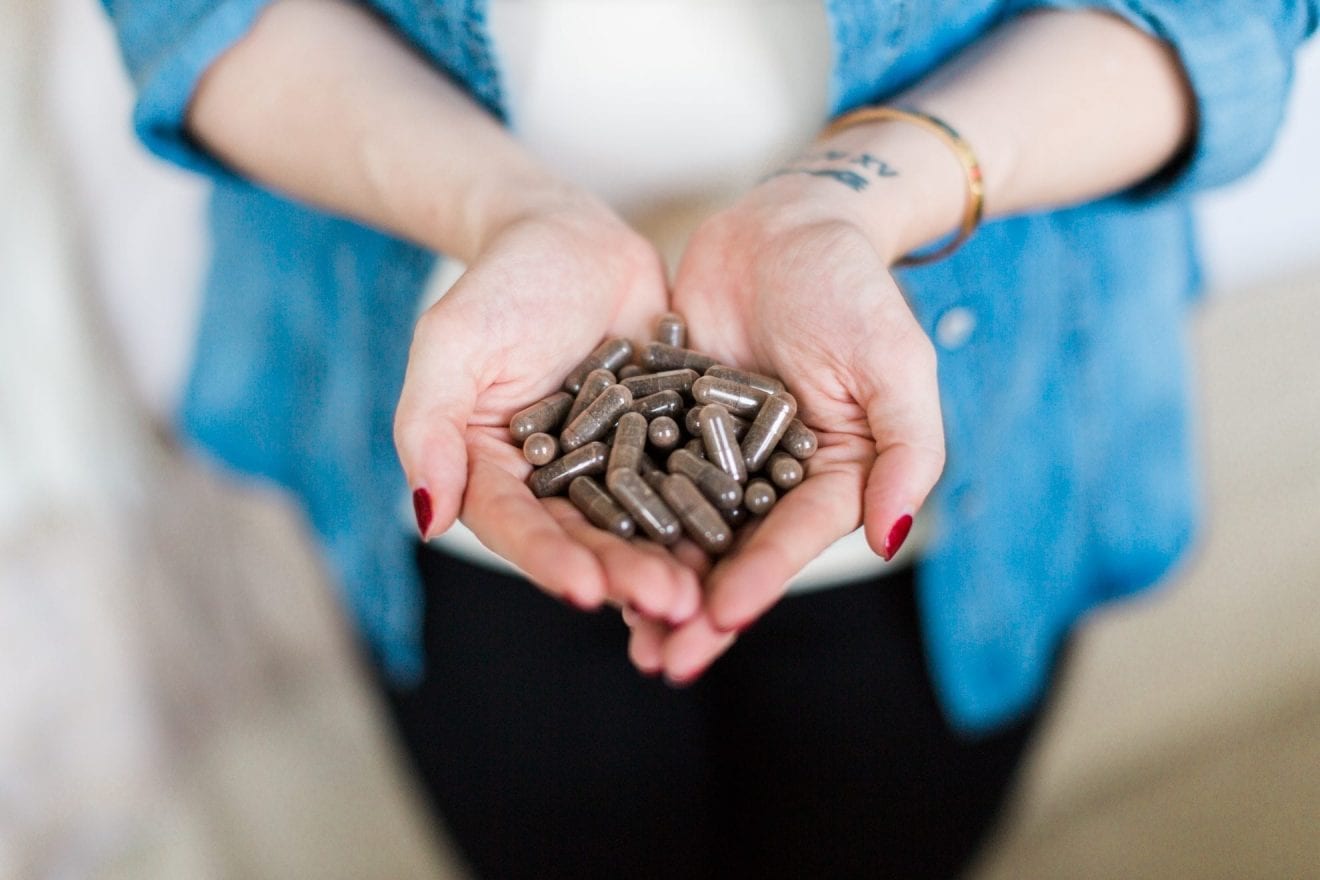
Placenta encapsulation is a process in which, immediately following the birth of your baby, your placenta is taken, cleaned, dehydrated, and ground into a coarse powder. The powder is then placed into small capsules that look like any other vitamin or supplement we might take. The capsules are then given to the mother to ingest for the next few weeks or months after the birth.
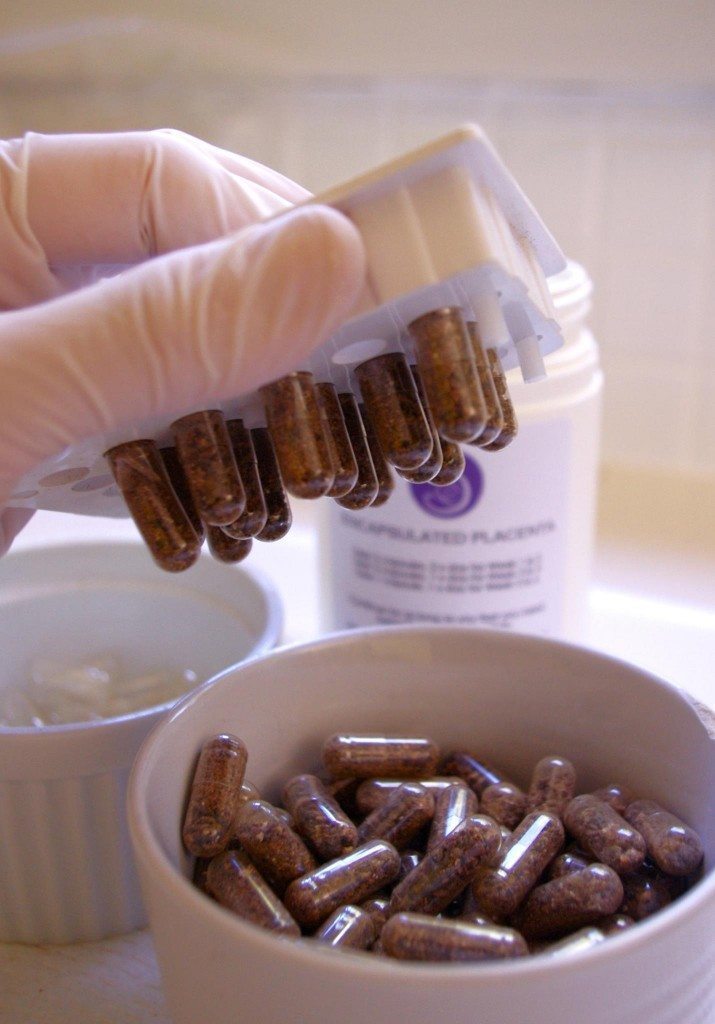

Why would a mother want to consume her placenta?
Some believe there are numerous health benefits from consuming the placenta. The placenta contains many crucial hormones and iron that leave a woman’s body once the placenta is born. Humans are one of the few mammals that do not eat their placentas. There is a practice known as placentophagia, where it is believed that consuming the placenta can help new mothers maintain their hormone and iron levels in the few weeks after birth.5 According to claims, this can speed up healing and help curb fatigue and anxiety in new mothers.
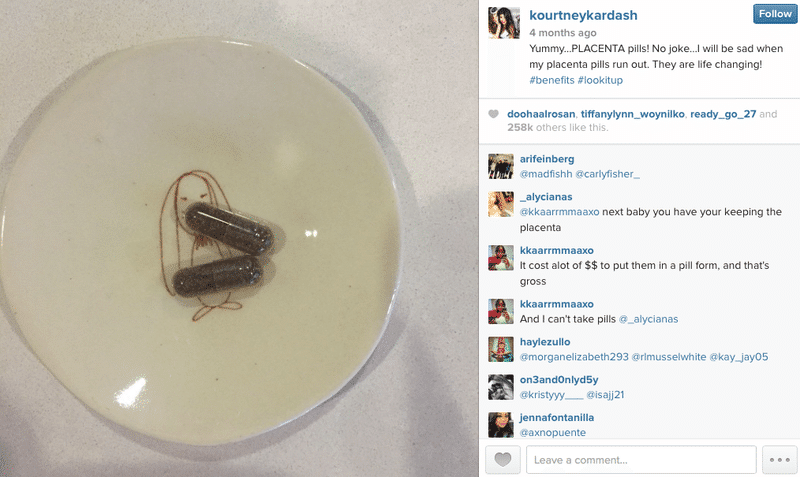
This practice has gained a lot of traction since some celebrities have encapsulated their placentas. Alicia Silverstone, who we all remember as Cher in the 90’s comedy “Clueless,” said that she ate her placenta after giving birth. Actress January Jones from “Mad Men” did the same. Kourtney Kardashian from “Keeping Up with the Kardashians” shared on her Instagram her placenta pills (aka “happy pills”) and how they have been “life-changing.”

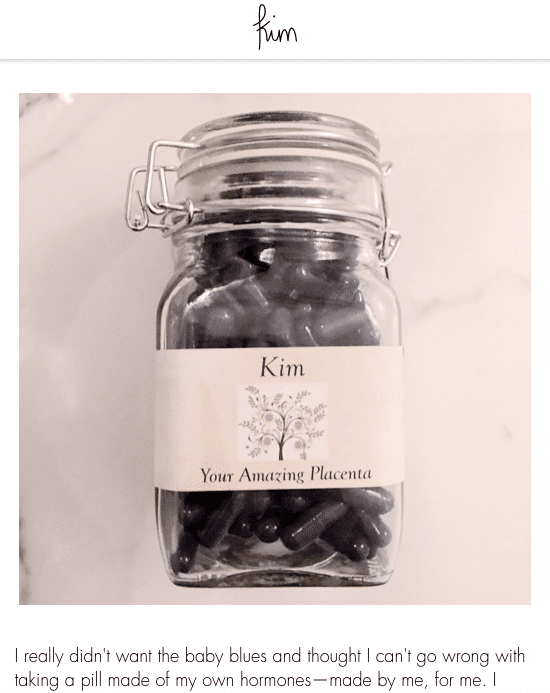
Even her sister, Kim Kardashian, shared on her website that she got her placenta encapsulated after the birth of her second child, Saint West.

What are the placenta encapsulation benefits?
There is little scientific research regarding placental encapsulation, its consumption, and its benefits. Additionally, there is no evidence eating the placenta provides health benefits.4 However, some websites and sources claim there are several potential advantages. Some of them are:
- Increased release of the hormone oxytocin. This helps the uterus return to normal size, reduces postpartum bleeding, and encourages bonding with the infant.
- Increase in CRH, a stress-reducing hormone
- A decrease in postpartum depression levels and “baby blues.”
- Increases the mother’s energy levels
- Restoration of iron levels in the blood
- Increase in milk production
How can placentophagia help curb postpartum mood problems?
Research published in The Journal of Nutrition shows that postpartum iron deficiency (anemia) can cause postpartum depression and postpartum anxiety.6 A study published in The Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology also indicates that fatigue is one of the major causes of postpartum depression.7 Many mothers report that consuming the placenta can boost energy levels. However, research suggests that encapsulated placenta supplementation neither significantly improves nor impairs postpartum maternal iron status for women consuming the RDA of dietary iron during pregnancy and lactation, compared to a beef placebo.8
How do I get my placenta encapsulated?
Yes, you can choose to dehydrate and encapsulate your placenta yourself. However, most people hire a placenta encapsulation specialist. A placenta professional will typically have specialized training and equipment to process the placenta and follow the OSHA safety guidelines for exposure to bloodborne pathogens.9 Most often, the placenta professional in your area is probably a doula, midwife, or other birth worker professional who works closely with birthing mothers.
Generally, your placenta professional will pick up your placenta from your birthplace (whether at the hospital, birth center, or your home) and process it in their workspace on special equipment reserved for placentas only. The placenta pills are usually dropped off to the mother within 2-3 days. Or they can be picked up from the placenta professional and stored in the refrigerator or freezer.
Here’s a video of a tour I took at a commercial-grade placenta encapsulation kitchen located in Houston, TX:
What are the methods for encapsulation?
There are two main methods for encapsulation, and before hiring a professional, you should ask which methods they offer so you can choose the one you prefer. Each recipe has pros and cons.
RAW Method
This method delivers the highest potency of the pills. This is because it is not cooked before it’s dried, but these pills expire after approximately one year of freezer storage.
Traditional Chinese Medicine Method
This recipe creates a pill that can be stored indefinitely with proper refrigeration. However, it is less potent than the raw form. Some women want to save their pills for when they have difficult menstrual cycles or for when they experience menopause. This is then the method they should choose.
How often should I take my placenta pills?
With placenta encapsulation, the placenta is steamed, dehydrated, and ground into 35 to 70 capsules. The number of capsules will vary depending on the size and thickness of the placenta. Most specialists recommend one capsule in the morning and one in the afternoon. Typically, you take them for about three weeks or until you run out. This amount gives the body a chance to heal and restore itself.
It’s been said that taking too many placenta pills daily can make women hyper-stimulated, nervous, and unable to sleep. Like they have had several energy drinks. Moms must understand that the placenta pills are meant to restore them and keep them feeling calm and balanced. They are not intended to reinvigorate them.

The Bottom Line…
There is little research available to support the benefits of placental encapsulation. And it is recommended that a placenta should not be encapsulated or ingested when there is an infection (chorioamnionitis) or if the placenta has been touched by meconium, the baby’s first poop.10 There are several proposed benefits of this custom and limited risks if the placenta is stored correctly and ingested only by the mother. Many doctors typically see consuming the placenta as an issue of harmless patient choice. However, the Centers for Disease Control has published a report of an infant who contracted an infection traced back to maternal consumption of capsules containing dehydrated placenta.3
I hope this answers many of the questions you had about placenta encapsulation. I would love to hear any stories of women who have done it, whether good or bad.































