As a mom-to-be, you might wonder what foods you should or shouldn’t eat to nourish your body and growing baby. One crucial nutrient that often goes unnoticed in pregnancy is iodine.
Understanding what iodine is, its significance during pregnancy, recommended intake during pregnancy, and iodine-rich food sources is vital so you know exactly how, why, and where to get it from your diet. And this will empower you to make informed choices for a healthy pregnancy journey.
What Is Iodine?
Iodine is an essential mineral that plays a significant role in thyroid hormones, crucial in regulating metabolism and promoting healthy brain development.1 It is not produced naturally by the body, so we rely on external sources — food — to meet our iodine needs.
Iodine is primarily found in seawater and soil, making its way into the food chain through marine plants and animals.2 This vital mineral is present in various food sources, and our bodies absorb it efficiently to support healthy growth and development.
Why Is Iodine Important During Pregnancy?
During pregnancy, iodine plays a critical role in the healthy development of your baby’s brain and nervous system. Adequate iodine levels are necessary to ensure proper thyroid function in the mother and the growing fetus.3 Thyroid hormones are essential for regulating metabolism, promoting normal growth, and supporting cognitive function.1
Insufficient iodine intake during pregnancy can lead to iodine deficiency disorder. Iodine deficiency poses a significant risk to a developing baby, potentially resulting in intellectual disabilities, hearing impairments, and stunted growth.4,5,6 Furthermore, low iodine levels may increase the risk of miscarriage, stillbirth, and preterm birth.7
How Much Iodine Do You Need During Pregnancy?
The recommended daily iodine intake for pregnant women is almost double that for the general population. The World Health Organization (WHO) suggests an intake of 250 micrograms (mcg) of iodine daily during pregnancy. This higher requirement compensates for the increased demands on the mother’s thyroid gland and ensures optimal iodine levels for fetal development.8
Low Iodine in Pregnancy and Iodine Deficiency During Pregnancy
Iodine deficiency during pregnancy is a pressing concern, as studies indicate it affects a significant portion (35-45%) of the global population. Factors such as geographical location, dietary habits, and iodine availability in the local environment can contribute to iodine deficiency.
As previously mentioned, iodine deficiency during pregnancy can have severe consequences. It is crucial to be aware of the signs and symptoms of iodine deficiency, which may include fatigue, weight gain, pregnancy constipation, swelling in the neck (indicating an enlarged thyroid gland, known as a goiter), and cognitive impairments.9
Foods High and Low in Iodine
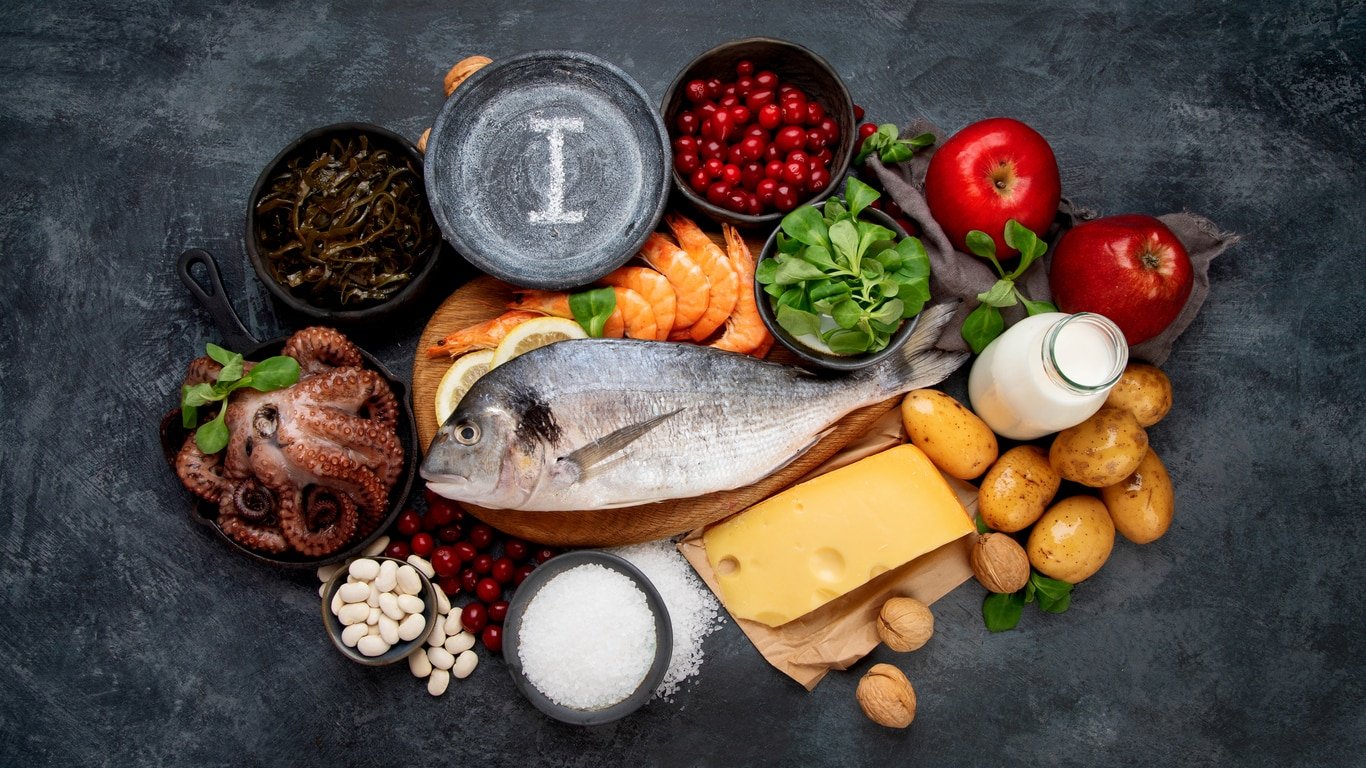

To ensure adequate iodine intake, including iodine-rich foods in your diet throughout pregnancy is essential.
Excellent sources of iodine include:10
- Seafood, such as fish, shellfish, and seaweed
- Dairy products like yogurt, milk, and cheese
- Eggs
- Iodized salt
Including these foods in your meals throughout the day can help maintain optimal iodine levels and support the healthy development of your baby.
Certain foods may interfere with iodine absorption or contain substances known as goitrogens that can reduce iodine levels in the body. Some foods that may affect iodine status include:11
- Cruciferous vegetables, such as broccoli, cabbage, and cauliflower
- Soy products, including tofu, soy milk, and other soy-based foods
- Some fruits, such as peaches, strawberries, and spinach
While these foods have nutritional benefits, balancing their consumption with iodine-rich foods is essential.
Can You Get Too Much Iodine?
While ensuring adequate iodine intake is crucial, it’s also important not to exceed recommended levels. Like iodine deficiency, consuming excessive amounts of iodine can have adverse effects. High iodine levels may disrupt thyroid function and lead to hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.12 Avoiding excessive iodine intake during pregnancy is especially important, as it can harm both the mother and the developing baby. Balancing iodine consumption is critical to maintaining optimal health.
As a mom-to-be, ensuring adequate iodine in pregnancy is essential not only for your health but for the optimal development of your baby. Maintaining proper levels of iodine throughout your pregnancy journey is paramount to mitigate the risks of iodine deficiency disorder, which can adversely affect your baby’s cognitive development and overall health. By incorporating iodine-rich foods into your diet and avoiding excessive intake, you can have a thriving pregnancy while giving your baby a healthy start. Remember to consult with your healthcare provider to assess your iodine levels and discuss any concerns or specific dietary recommendations.